- Physical Examination
- Surgical Examination
- Ophthalmology
- Clinical Skills
- Orthopedics
- Surgery Videos
- Laparoscopy
- Pediatrics
- Funny Videos
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Nursing Videos
- Plastic Surgery
- Otorhinolaryngology
- Histology and Histopathology
- Neurosurgery
- Dermatology
- Pediatric Surgery
- Urology
- Dentistry
- Oncology and Cancers
- Anatomy Videos
- Health and Fitness
- Radiology
- Anaesthesia
- Physical Therapy
- Pharmacology
- Interventional Radiology
- Cardiology
- Endocrinology
- Gynecology
- Emergency Medicine
- Psychiatry and Psychology
- Childbirth Videos
- General Medical Videos
- Nephrology
- Physiology
- Diet and Food Health
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Neurology
- Women Health
- Osteoporosis
- Gastroenterology
- Pulmonology
- Hematology
- Rheumatology
- Toxicology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Vascular Disease
- Reproductive Health
- Burns and Wound Healing
- Other
HIV / AIDS
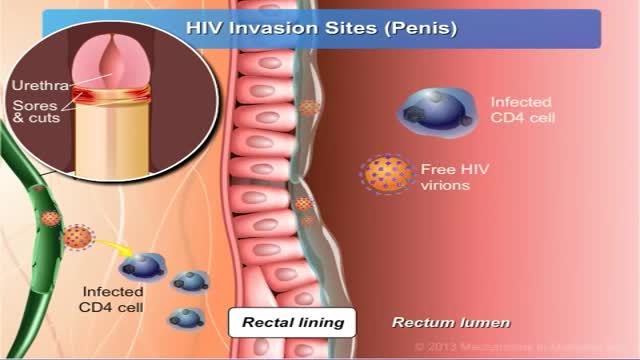
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely. So once you have HIV, you have it for life. HIV attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which help the immune system fight off infections. If left untreated, HIV reduces the number of CD4 cells (T cells) in the body, making the person more likely to get infections or infection-related cancers. Over time, HIV can destroy so many of these cells that the body can’t fight off infections and disease. These opportunistic infections or cancers take advantage of a very weak immune system and signal that the person has AIDS, the last state of HIV infection. No effective cure for HIV currently exists, but with proper treatment and medical care, HIV can be controlled. The medicine used to treat HIV is called antiretroviral therapy or ART. If taken the right way, every day, this medicine can dramatically prolong the lives of many people with HIV, keep them healthy, and greatly lower their chance of transmitting the virus to others. Today, a person who is diagnosed with HIV, treated before the disease is far advanced, and stays on treatment can live a nearly as long as someone who does not have HIV.